RAD Model
Definition:
The RAD Model (Rapid Application Development) is a type of software development model that focuses on fast delivery of a working software product using short development cycles and rapid prototyping.
Instead of planning and building everything at once (like the waterfall model), RAD builds the software in small parts quickly, with continuous user feedback.
Objectives of RAD Model:
To develop software faster than traditional methods.
To involve users actively during development.
To reduce development time using reusable components.
To allow quick delivery with working prototypes.
Features of the RAD Model:
Software is developed in modules or components quickly.
Prototypes are created and shown to users for feedback.
Emphasizes speed over perfection.
Uses reusable tools and pre-built components.
Requires strong team collaboration and user involvement.
Best suited for short and fast-paced projects.
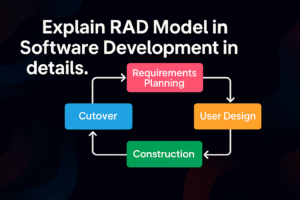
Phases of the RAD Model:-
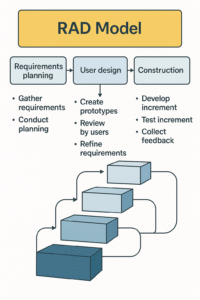
1. Business Modeling
What happens in this phase:
Understand the business or organization where the software will be used.
Identify business functions like sales, finance, support, etc.
Find out what information flows between these functions.
Why it’s important:
It gives a clear view of how the software will support real-life business needs.
2. Data Modeling
What happens in this phase:
Identify the data required by the system.
Decide how data will be stored, organized, and related.
Create Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) or other data flow representations.
Why it’s important:
This helps to design a strong database and avoid data errors or duplication
3. Process Modeling
What happens in this phase:
Define the processes (actions) that the software will perform using the data.
Map out how data moves from one step to another.
Make flowcharts or data process diagrams.
Why it’s important:
Shows how users interact with data and how data changes in the system.
4. Application Generation
What happens in this phase:
Developers use automated tools, frameworks, or pre-built components to quickly create software modules.
Prototypes are built and tested by users.
Any changes or improvements suggested are applied immediately.
Why it’s important:
Fast creation of software using reusable code speeds up development.
5. Testing and Turnover
What happens in this phase:
The system is tested for functionality, performance, and errors.
Since modules are built separately, testing is done in parts (unit testing) and as a whole (integration testing).
Once confirmed, the software is handed over (delivered) to users.
Why it’s important:
Ensures the software works well, meets user needs, and is ready for real-world use.
Advantages of the RAD Model:
Fast development and delivery.
Early user feedback through prototypes.
Reduces risk by allowing changes early.
Encourages team collaboration.
More productivity due to reusable components.
Disadvantages of the RAD Model:
Not suitable for large-scale or complex projects.
Needs highly skilled developers and designers.
Depends on constant user involvement.
Difficult to manage if project size increases.
Less focus on documentation.
Best Use Cases for the RAD Model:
When you need software quickly (e.g., internal tools).
When requirements are changing or not fixed.
When users are available for feedback during development.
Examples:
Prototypes for apps or websites.
Government forms, surveys, portals.
Rapid mobile app development.
RAD MODEL IN HINGLISH
Definition (परिभाषा):
RAD Model एक ऐसा software development तरीका है जिसमें software को बहुत तेज़ी से (fast) और छोटे-छोटे भागों (modules) में develop किया जाता है। इसमें बार-बार feedback लेकर prototype तैयार किया जाता है।
Waterfall model की तरह सब कुछ एक बार में नहीं बनाया जाता, बल्कि RAD model में software को टुकड़ों में जल्दी-जल्दी बनाकर user को दिखाया जाता है।
Objectives (उद्देश्य):
Software को traditional method से ज़्यादा तेज़ बनाना।
Development के दौरान users की active भागीदारी।
Reusable components का use करके time बचाना।
Working prototype जल्दी देना।
Features (विशेषताएँ):
Software को components में divide करके develop किया जाता है।
हर stage पर prototype बनाकर user से feedback लिया जाता है।
Focus होता है speed पर, perfection बाद में आती है।
Tools और ready-made components का इस्तेमाल होता है।
Teamwork और client की involvement ज़रूरी होती है।
यह method short और fast projects के लिए best है।
Phases (चरण)
1. Business Modeling (बिज़नेस मॉडलिंग)
क्या होता है:
यह समझना कि software किस काम को support करेगा।
Organization के departments और उनकी जानकारी की needs जानना।
Data का flow कैसे होता है, उसे analyze करना।
क्यों ज़रूरी है:
ताकि software business की real जरूरतों को fulfill कर सके।
2. Data Modeling (डेटा मॉडलिंग)
क्या होता है:
System में कौन-कौन सा data चाहिए, उसे पहचानना।
Data कैसे store होगा, linked होगा – इसकी planning करना।
ER Diagram और data flow diagram बनाना।
क्यों ज़रूरी है:
एक मजबूत database बनता है और data duplication से बचा जा सकता है।
3. Process Modeling (प्रोसेस मॉडलिंग)
क्या होता है:
यह define करना कि system data के साथ क्या-क्या actions करेगा।
Data एक step से दूसरे step में कैसे जाएगा – इसका flowchart बनाना।
क्यों ज़रूरी है:
यह समझना कि user और system कैसे data को process करते हैं।
4. Application Generation (एप्लिकेशन जनरेशन)
क्या होता है:
Ready tools और components की मदद से जल्दी software बनाना।
Prototype बनाना और user से feedback लेना।
Feedback के हिसाब से तुरंत सुधार करना।
क्यों ज़रूरी है:
इससे development तेज़ होता है और user को working model जल्दी दिखता है।
5. Testing and Turnover (टेस्टिंग और डिलीवरी)
क्या होता है:
बने हुए modules की testing करना।
Integration testing करके सभी parts को जोड़ना।
जब सब कुछ ठीक हो, तब final product user को देना।
क्यों ज़रूरी है:
Software bugs-free और ready-to-use हो।
Advantages (फायदे):
तेज़ delivery और development।
User से feedback जल्दी मिलता है।
Requirement में बदलाव जल्दी किया जा सकता है।
Component reuse से productivity बढ़ती है।
Team और client का collaboration अच्छा होता है।
Disadvantages (नुकसान):
बड़े और complex projects के लिए ठीक नहीं।
Skilled developers की ज़रूरत होती है।
User का बार-बार available रहना ज़रूरी होता है।
Documentation पर कम ध्यान दिया जाता है।
अगर project बढ़ता है, तो management मुश्किल हो सकता है।
Best Case for Use (उपयोग के सबसे अच्छे मामले):
जब software बहुत जल्दी चाहिए हो।
जब requirements बार-बार बदलती हो।
जब client हर stage पर feedback दे सकता हो।
Examples:
Prototypes और apps.
Online forms या survey systems.
जल्दी बनने वाले mobile apps.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.