Prototype Model
Definition
The Prototype Model is a software development model where a quick working version (prototype) of the software is created before building the final system. This prototype shows how the final software will look and behave.
Users check the prototype, give feedback, and developers improve it. This process is repeated until the user is fully satisfied.
Objectives of the Prototype Model:
- To understand user needs better.
- To reduce miscommunication between users and developers.
- To provide an early model for feedback and improvement.
- To save time and effort by finding problems early.
Features of the Prototype Model:
- A temporary version (mock-up) of the software is created.
- User feedback is collected early and often.
- Focus is on interface, design, and flow, not full functionality.
- It is an interactive process — change and test again.
- The final system is developed after multiple improvements.
Phases of the Prototype Model
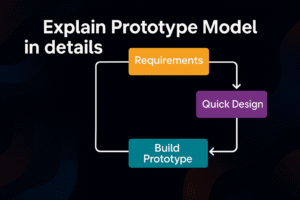
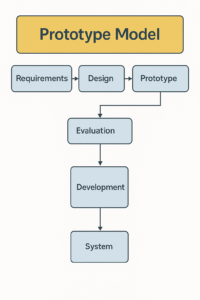
1. Requirements Gathering:
- Basic requirements are collected from the user.
- The focus is on what the user wants to see and use.
- Not all features are finalized — just the important ones for the prototype.
2. Quick Design:
- A basic design of the software is created.
- This includes the user interface (UI), menus, forms, screens, etc.
- No deep coding — just visual structure and layout.
3. Prototype Building:
- The actual prototype is built using tools or rapid coding.
- It works like a model of the real system — just enough to demonstrate.
- It’s not the full system; it’s just for demonstration.
4. User Evaluation:
- Users try the prototype and give feedback.
- They share what they like, don’t like, or want to change.
- Developers collect this feedback for improvement.
5. Refinement:
- Developers improve the prototype based on user feedback.
- The process repeats — redesign, review, and refine — until the user is satisfied.
6. Final Product Development:
- Once the prototype is approved, the real system is developed.
- Full coding, testing, and implementation are done.
- The final product is more accurate, as it is based on tested ideas.
Advantages of the Prototype Model:
- Helps understand actual user needs.
- Reduces chances of requirement errors.
- Saves time and cost by finding problems early.
- Builds user confidence and satisfaction.
- Allows changes during development.
Disadvantages of the Prototype Model:
- Too much focus on prototype can delay final product.
- Sometimes users think the prototype is the real product.
- Not suitable for large and complex systems.
- Developers may spend extra time refining a throwaway model.
- Poorly planned prototypes can lead to confusion.
Best Use Cases for the Prototype Model:
- When requirements are not clear at the beginning.
- When the user needs to “see” the software to understand.
- For user-interface heavy systems like:
- Mobile apps
- E-commerce platforms
- Online forms and dashboards
- Custom software for clients
Prototype model in Hinglish
Definition (परिभाषा):
Prototype Model एक ऐसा software development तरीका है जिसमें एक जल्दी तैयार किया गया working version (prototype) सबसे पहले बनाया जाता है।
यह prototype दिखाता है कि final software कैसा दिखेगा और कैसे काम करेगा।
User उसे देखकर feedback देता है, और developer उसमें बदलाव करता है। यह process बार-बार दोहराई जाती है जब तक user पूरी तरह से संतुष्ट न हो जाए।
Prototype Model के Objectives (उद्देश्य):
User की ज़रूरतों को सही से समझना।
Developer और user के बीच confusion को कम करना।
Feedback लेने के लिए जल्दी एक model देना।
शुरू में ही गलती पकड़कर time और मेहनत बचाना।
Prototype Model की Features (विशेषताएँ):
Software का एक temporary version बनाया जाता है।
User का feedback बार-बार लिया जाता है।
Focus होता है design, layout, और flow पर, ना कि पूरी functionality पर।
यह एक interactive process होता है – change करो, फिर test करो।
Final system prototype को कई बार सुधारने के बाद बनाया जाता है।
Prototype Model के Phases
1. Requirements Gathering (ज़रूरतें इकट्ठा करना):
User से basic ज़रूरतें पूछी जाती हैं।
सिर्फ़ जरूरी functions लिए जाते हैं, सभी नहीं।
Focus होता है कि user क्या देखना और इस्तेमाल करना चाहता है।
2. Quick Design (जल्दी design बनाना):
एक simple design तैयार किया जाता है।
UI, menus, forms, और screens जैसी चीज़ों को visual रूप में दिखाया जाता है।
इसमें गहराई से coding नहीं होती – सिर्फ layout।
3. Prototype Building (प्रोटोटाइप बनाना):
Prototype tools या जल्दी coding से बनाया जाता है।
यह real system जैसा दिखता है, पर पूरी तरह से काम नहीं करता।
सिर्फ़ दिखाने और समझाने के लिए बनाया जाता है।
4. User Evaluation (User द्वारा जाँच):
User prototype को इस्तेमाल करके feedback देता है।
वह बताता है कि उसे क्या पसंद आया, क्या बदलना है।
Developer इस feedback को improve करने के लिए उपयोग करता है।
5. Refinement (सुधार करना):
Feedback के आधार पर prototype में बदलाव किए जाते हैं।
यह process बार-बार दोहराई जाती है जब तक user संतुष्ट नहीं होता।
6. Final Product Development (Final software बनाना):
जब user prototype से संतुष्ट होता है, तब असली system develop किया जाता है।
अब full coding, testing, और launch किया जाता है।
Final product ज़्यादा accurate होता है क्योंकि वो tested ideas पर based होता है।
Advantages (फायदे):
User की असली ज़रूरतें जल्दी समझ में आती हैं।
Requirement errors कम होते हैं।
Problems शुरू में ही पकड़ में आ जाती हैं, time और cost बचती है।
User का confidence बढ़ता है।
Development के दौरान changes आसानी से किए जा सकते हैं।
Disadvantages (नुकसान):
Prototype पर ज़्यादा ध्यान देने से final product delay हो सकता है।
कुछ users समझते हैं कि prototype ही final product है।
बड़े या complex systems के लिए यह model सही नहीं है।
Throwaway model पर ज़्यादा time लग सकता है।
खराब planning से confusion हो सकता है।
Best Use Cases (कब उपयोग करें):
जब शुरुआत में requirements clear ना हों।
जब user को software देख कर ही समझ आता हो।
Interface-heavy systems के लिए जैसे:
Mobile Apps
E-commerce Sites
Online Forms & Dashboards
Customized Client Software
Computer Study Notes is a really helpful website for students and beginners. The concepts are explained in very simple and clear language, which makes learning computers easy and stress-free. It is perfect for exam preparation and building strong basics.