Unified Process (UP)
Definition:
The Unified Process (UP) is a software development process framework that is use-case driven, architecture-centric, and iterative & incremental.
It was developed to organize and manage complex software projects by breaking the development into phases and repeating cycles (iterations).
It is the foundation of the Rational Unified Process (RUP) developed by Rational Software (now part of IBM). The process focuses on early risk reduction, continuous feedback, and strong architecture.
Objectives of Unified Process:
To break the project into manageable steps (iterations) for better control and quality.
To ensure user involvement throughout the development for accurate requirements.
To focus on building a solid system architecture before diving into full development.
To reduce project risks early by addressing them in the initial phases.
To deliver working software regularly, not just at the end.
To support continuous testing and refinement of the software.
Features of Unified Process:
Iterative and Incremental Development:
The system is developed in multiple cycles, and each cycle adds more features.Use-Case Driven Approach:
Requirements are collected and analyzed based on user use cases (real-world usage scenarios).Architecture-Centric:
The system’s core structure (architecture) is designed early and developed carefully.Risk Management:
Risks are identified and reduced early during development, especially in the elaboration phase.Continuous Testing:
Testing is done throughout the development in every iteration, not just at the end.Disciplined Methodology:
The process is well-organized, with clear phases, roles, and deliverables.
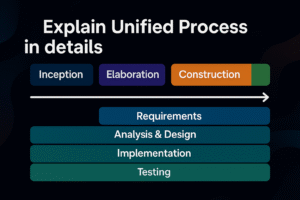
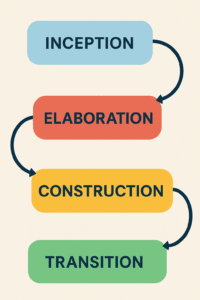
Phases of Unified Process:
1. Inception Phase:
Define the basic idea and goal of the project.
Identify key stakeholders and use cases.
Estimate the cost, schedule, and risks.
Create a project plan and business case.
Result: Initial project vision and feasibility study.
2. Elaboration Phase:
Analyze and refine requirements in more detail.
Design and implement a core architecture.
Build a prototype or partial system to test feasibility.
Identify and address technical and design risks.
Result: A stable software architecture and updated project plan.
3. Construction Phase:
Develop the complete product features and functions.
Perform coding, integration, and testing.
Build the system in multiple iterations.
Prepare for user deployment.
Result: A fully functional and tested software product.
4. Transition Phase:
Deploy the final product to the end users.
Fix remaining bugs and performance issues.
Provide user training and support.
Collect user feedback for future updates.
Result: A final, stable release ready for real-world use.
Advantages of Unified Process:
Helps manage complex and large projects effectively.
Encourages early detection and resolution of risks.
Supports regular user feedback, improving product quality.
Builds a solid architectural foundation, reducing future problems.
Testing in each iteration leads to fewer bugs and higher quality.
Changes in requirements can be handled flexibly over iterations.
Promotes reusability of components and models.
Disadvantages of Unified Process:
It can be too complex and heavy for small or simple projects.
Needs a well-trained and experienced team to follow all phases properly.
Planning and documentation can take a lot of time and effort.
Requires strict discipline in following the process, otherwise it may fail.
May result in increased development cost if not managed well.
Best Cases to Use Unified Process:
When the project is large-scale and complex.
When the software requires high reliability, quality, and security.
When the requirements are unclear or may change over time.
When the client demands early working versions of the software.
When the development team is skilled and organized.
Suitable for mission-critical applications like in banking, healthcare, aerospace, etc.
Unified Process (UP) IN Hinglish
परिभाषा (Definition):
- Unified Process (UP) एक Software Development Framework है जो कि
➤ Use-case driven,
➤ Architecture-centric,
➤ और Iterative & Incremental होता है। - इसका उद्देश्य है कि बड़े और जटिल projects को छोटे-छोटे phases और iterations में divide कर के develop किया जाए।
- यह Rational Unified Process (RUP) का आधार है, जिसे Rational Software (अब IBM का हिस्सा) ने बनाया।
- यह प्रक्रिया early risk management, continuous feedback और strong system architecture पर focus करती है।
Unified Process के उद्देश्य (Objectives):
- Project को manageable steps (iterations) में divide करना ताकि control और quality बनी रहे।
- पूरे development के दौरान user involvement सुनिश्चित करना।
- Full development से पहले एक strong architecture तैयार करना।
- शुरू में ही project risks को पहचानकर उन्हें reduce करना।
- केवल अंत में नहीं, बल्कि regularly working software deliver करना।
- Continuous testing और improvement को support करना।
Unified Process की विशेषताएँ (Features):
- Iterative & Incremental Development:
System को बार-बार दोहराकर develop किया जाता है और हर iteration में नया हिस्सा जोड़ा जाता है। - Use-Case Driven:
Requirements को real-world user scenarios (use cases) के आधार पर collect किया जाता है। - Architecture-Centric:
Project की शुरुआत में ही एक strong architecture design किया जाता है। - Risk Management:
Elaboration phase में ही technical और project-related risks को identify और control किया जाता है। - Continuous Testing:
हर iteration में testing की जाती है, जिससे bugs जल्दी पकड़ में आते हैं। - Disciplined Approach:
इसमें साफ-सुथरी planning, roles और deliverables तय होते हैं।
Unified Process के चार प्रमुख चरण (Phases):
Inception Phase (आरंभ चरण):
- Project का main idea और objective समझना।
- Key stakeholders और use-cases को पहचानना।
- Cost, time, और risk का अनुमान लगाना।
- एक प्राथमिक project plan और business case बनाना।
Output: Vision document और प्रारंभिक feasibility report।
Elaboration Phase (विस्तार चरण):
- Requirements को और गहराई से analyze करना।
- System architecture design और implement करना।
- एक छोटा prototype बनाना।
- Risks को पहचानना और handle करना।
Output: Stable architecture और refined project plan।
Construction Phase (निर्माण चरण):
- Product की main functionality और features को develop करना।
- Coding, integration और testing करना।
- Multiple iterations में पूरा system बनाना।
- Deployment के लिए तैयारी करना।
Output: Fully functional और tested software।
Transition Phase (स्थानांतरण चरण):
- Final product को users तक पहुँचाना।
- बचे हुए bugs और performance issues को fix करना।
- Users को training देना और support देना।
- Feedback collect करना future updates के लिए।
Output: Final stable release।
Unified Process के फ़ायदे (Advantages):
- बड़े और जटिल projects को manage करने में मदद मिलती है।
- शुरू में ही risks का पता चल जाता है और उन्हें control किया जा सकता है।
- Regular feedback से product की quality बढ़ती है।
- Architecture पहले बन जाने से future में technical problems कम होती हैं।
- हर iteration में testing होने से bugs जल्दी मिलते हैं।
- Changing requirements को आसानी से manage किया जा सकता है।
- Components और models को reuse किया जा सकता है।
Unified Process के नुकसान (Disadvantages):
- छोटे और simple projects के लिए यह process बहुत heavy हो सकता है।
- इसे follow करने के लिए skilled और trained team की जरूरत होती है।
- Planning और documentation में बहुत समय लग सकता है।
- Process को strict discipline से follow करना जरूरी है, नहीं तो failure हो सकता है।
- Proper management न हो तो cost बढ़ सकती है।
Unified Process कब Use करें? (Best Case to Use):
- जब project large-scale और complex हो।
- जब system को high reliability, quality और security चाहिए।
- जब requirements शुरू में clear ना हों या बदल सकती हों।
- जब client जल्दी working software देखना चाहता हो।
- जब development team organized और skilled हो।
- जब application mission-critical हो – जैसे banking, medical, या aerospace projects।