Measure in Software

1. Definition of Software Measure
- A software measure is the act of finding the size, quantity, or degree of a software attribute.
- It is the actual value we get when we measure something in software development.
- Example: If “Lines of Code” is a metric, then 500 LOC is the measure.
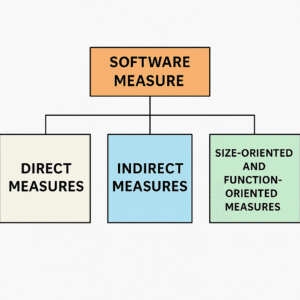
2. Types of Software Measures
Software measures can be divided into three main types:
A. Direct Measures
- These measure software attributes directly without using any other calculation.
- Examples:
- Number of lines of code
- Execution time
- Number of defects found
- Memory usage
B. Indirect Measures
- These are calculated using two or more direct measures.
- They are derived values.
- Examples:
- Defect density = Number of defects / Size of software
- Productivity = LOC / Person-hours
C. Size-Oriented and Function-Oriented Measures
- Size-Oriented → Based on the physical size of software (e.g., LOC, bytes).
- Function-Oriented → Based on the functionality delivered to the user (e.g., Function Points).
3. Applications of Software Measures
- Project Estimation
- Help estimate cost, time, and effort required.
- Quality Control
- Measure quality by tracking defects and performance.
- Performance Monitoring
- Measure speed, memory, and processing efficiency.
- Risk Management
- Identify areas with high defect rates or poor performance.
- Process Improvement
- Compare past and current measures to improve development methods.
- Team Productivity Tracking
- Measure output per developer to improve efficiency.
4. Features of Good Software Measures
- Accuracy
- Should reflect the real value of the attribute being measured.
- Objectivity
- Should be based on facts, not opinions.
- Repeatability
- Should give the same result if measured again under the same conditions.
- Simplicity
- Should be easy to understand and calculate.
- Relevance
- Should be related to project or product goals.
- Comparability
- Should help in comparing results across projects.
- Action-Oriented
- Should help make decisions for improvement.
Measure in Hinglish
1. Definition of Software Measure (परिभाषा)
- Software Measure का मतलब है software attribute (जैसे size, quantity, performance) को नापना या मापना।
- ये वो actual value होती है जो हमें measure करने के बाद मिलती है।
- Example: अगर “Lines of Code (LOC)” एक metric है और कोड में 500 lines हैं, तो 500 LOC ही हमारा measure है।
2. Types of Software Measures (प्रकार)
A. Direct Measures (सीधा माप)
- वो measure जो सीधे लिया जाता है, बिना किसी calculation के।
- Examples:
- Number of lines of code (LOC)
- Execution time (चलने का समय)
- Number of defects found (गलतियों की संख्या)
- Memory usage (मेमोरी का इस्तेमाल)
B. Indirect Measures (अप्रत्यक्ष माप)
- ये calculation से निकाले जाते हैं, मतलब 2 या उससे ज्यादा direct measures को मिलाकर।
- Examples:
- Defect density = Number of defects / Size of software
- Productivity = LOC / Person-hours
C. Size-Oriented & Function-Oriented Measures
- Size-Oriented (आकार आधारित) → Software के physical size पर आधारित (जैसे LOC, bytes)।
- Function-Oriented (कार्य आधारित) → Software के द्वारा user को दी जाने वाली functionality पर आधारित (जैसे Function Points)।
3. Applications of Software Measures (उपयोग)
- Project Estimation (परियोजना अनुमान)
- Cost, time, और effort का अनुमान लगाने में मदद।
- Quality Control (गुणवत्ता नियंत्रण)
- Defects और performance track करके quality मापना।
- Performance Monitoring (प्रदर्शन निगरानी)
- Speed, memory usage और processing efficiency मापना।
- Risk Management (जोखिम प्रबंधन)
- ऐसे हिस्सों को पहचानना जहां ज्यादा defects या खराब performance है।
- Process Improvement (प्रक्रिया सुधार)
- पुराने और नए measures compare करके development method सुधारना।
- Team Productivity Tracking (टीम की उत्पादकता ट्रैक करना)
- Developer की output मापकर efficiency बढ़ाना।
4. Features of Good Software Measures (अच्छे माप की विशेषताएँ)
- Accuracy (सटीकता) → असली value को सही तरीके से दर्शाए।
- Objectivity (वस्तुनिष्ठता) → Opinion नहीं, सिर्फ facts पर आधारित हो।
- Repeatability (दोहराव) → Same condition में वही result दे।
- Simplicity (सरलता) → समझने और calculate करने में आसान हो।
- Relevance (प्रासंगिकता) → Project या product goals से जुड़ा हो।
- Comparability (तुलनात्मकता) → Projects के बीच compare करने में मदद करे।
- Action-Oriented (क्रियात्मक) → Decision लेने में मदद करे।
Computer Study Notes website ne computer learning ko kaafi simple bana diya hai. Yahan updated content milta hai aur examples ke saath explanation diya gaya hai jo understanding ko aur strong karta hai.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.