Waterfall model with advantages disadvantages feature, with diagram
Definition:
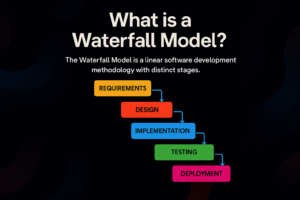
The Waterfall Model is one of the oldest and simplest models of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). In this model, each phase is completed one after the other in a linear and step-by-step manner, like water flowing down a waterfall.
You can’t go back to a previous phase once it is completed. So, each step must be finished before moving to the next.
Phases of the Waterfall Model:
Requirement Gathering – Understanding what the user needs.
System Design – Planning the structure and design of the software.
Implementation (Coding) – Writing the actual program.
Testing – Checking for bugs and errors.
Deployment – Releasing the software to users.
Maintenance – Fixing problems and updating software after release.
Objectives of the Waterfall Model:
To complete the software in a structured and step-by-step way.
To clearly define each phase of development.
To finish one phase fully before moving to the next.
To create well-documented software.
Features of the Waterfall Model:
Linear Sequence: All steps follow in order.
Rigid Structure: Cannot go back to a previous step.
High Documentation: Each phase has complete documents.
Clear Milestones: When one phase ends, the next begins.
Best for Short-Term Projects: Works well if the project is small and requirements are clear.
Advantages of Waterfall Model:
Simple and easy to use.
Well-structured and easy to manage.
Good for projects with fixed and clear requirements.
Phases do not overlap — easy to measure progress.
Each stage is well-documented.
Disadvantages of Waterfall Model:
Not flexible — you can’t go back to change something.
Not suitable for long or complex projects.
High risk if requirements change mid-project.
Late testing may delay detection of serious bugs.
No working software is available until the end.
Phases of the Waterfall Model (Step-by-Step with Details)
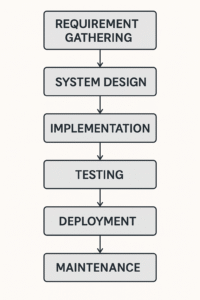
1. Requirement Gathering
What Happens in This Phase:
The client or user explains what they want the software to do.
Developers collect all needs and write them in a document called the Software Requirement Specification (SRS).
This includes: features, goals, user expectations, and system behavior.
Goal: Understand exactly what the user needs — because once this phase is done, changes are not allowed.
2. System Design
What Happens in This Phase:
Based on the requirements, the software design is prepared.
The design includes:
Architecture of the system.
Database design.
User interface design (what it will look like).
Data flow diagrams and technical plans.
Goal: Make a complete blueprint of how the software will work.
3. Implementation (Coding)
What Happens in This Phase:
Programmers start writing code based on the system design.
Each part (called a module) is built separately and then combined.
Developers follow the programming languages and tools decided in the design phase.
Goal: Convert the design into a real working program.
4. Testing
What Happens in This Phase:
The entire software is tested to check:
If it works correctly (called functional testing).
If it is fast and safe (called non-functional testing).
If there are bugs or errors.
Goal: Make sure the software is error-free and reliable before it goes to the user.
5. Deployment
What Happens in This Phase:
After successful testing, the software is installed on the user’s system.
It is now available for real users to use.
Sometimes, the team gives training or manuals.
Goal: Deliver the final software to the customer.
6. Maintenance
What Happens in This Phase:
After release, if users face problems or ask for updates, developers fix issues.
This includes:
Bug fixing.
Improving performance.
Adding new features.
Goal: Keep the software updated and working smoothly for a long time.
Best Case to Use the Waterfall Model:
When requirements are clear, fixed, and well-understood.
When the project is short-term and simple.
When the technology is well-known and there’s no expected change.
Examples:
Small internal tools.
College or academic projects.
Government or defense contracts with strict requirements
Waterfall Model Kya Hai? (Definition)
Waterfall Model software development ka सबसे पुराना और simple model है। इसमें सारे phases एक के बाद एक step-by-step complete होते हैं — जैसे पानी झरने से नीचे गिरता है।
👉 एक बार कोई phase complete हो गया, तो वापस नहीं जा सकते। मतलब पहले वाला step पूरा होना चाहिए, तभी अगला शुरू होगा।
Objectives of Waterfall Model (उद्देश्य):
- Software को step-by-step structured तरीके से बनाना।
- हर phase को clearly define करना।
- एक phase पूरी तरह complete होने के बाद ही अगले phase पर जाना।
- हर step की proper documentation रखना।
Features of Waterfall Model (मुख्य विशेषताएं):
- Linear Process: Phases ek order में होते हैं।
- Rigid Structure: वापस पुराने step पर नहीं जा सकते।
- High Documentation: हर phase की पूरी रिपोर्ट होती है।
- Clear Milestones: कब कौनसा phase complete हुआ — साफ़ दिखाई देता है।
- Best for Small Projects: जब requirements बिल्कुल clear हों।
Advantages (फायदे):
- Simple aur easy to understand model है।
- Manage करना आसान होता है।
- Jab requirements पहले से fix हों — बहुत अच्छा काम करता है।
- हर phase alag होता है — progress measure करना आसान होता है।
- अच्छी documentation मिलती है।
Disadvantages (नुकसान):
- Bilkul भी flexible नहीं — बाद में कुछ change नहीं कर सकते।
- Complex और लंबे projects के लिए ठीक नहीं।
- अगर बीच में requirement बदली, तो risk बहुत बढ़ जाता है।
- Testing बहुत late होती है — bugs आख़िर में मिलते हैं।
- End तक कोई working software नहीं दिखता।
Waterfall Model Ke Phases (Step-by-Step with Details):
Requirement Gathering (ज़रूरतें समझना)
Kya hota hai:
- User या client बताता है कि software को क्या करना है।
- Developer सारी information इकट्ठा करता है और एक document बनाता है — SRS (Software Requirement Specification)।
- इसमें features, expectations, goals सब होते हैं।
Goal: शुरू में ही पूरी clarity हो — बाद में changes allowed नहीं होंगे।
System Design (सिस्टम डिज़ाइन बनाना)
Kya hota hai:
- Requirement के हिसाब से पूरा system design किया जाता है।
- इसमें शामिल होते हैं:
- System architecture
- Database structure
- User interface design
- Flowcharts और diagrams
Goal: Software कैसे काम करेगा इसका पूरा नक्शा बनाना।
Implementation (Coding करना)
Kya hota hai:
- Design को देखकर coders programming शुरू करते हैं।
- Software को अलग-अलग modules में develop किया जाता है।
- Tools और languages वही होते हैं जो design phase में decide हुए थे।
Goal: Design को एक working software में बदलना।
Testing (जांच और परीक्षण)
Kya hota hai:
- Software को पूरी तरह test किया जाता है:
- Functional Testing — software सही से काम कर रहा या नहीं।
- Non-Functional Testing — speed, security, load, आदि।
Goal: Final product bug-free और reliable हो।
Deployment (रिलीज़ करना)
Kya hota hai:
- Testing के बाद software user के system पर install किया जाता है।
- Manual या training दी जाती है।
Goal: Software को customer तक पहुँचाना।
Maintenance (देखभाल और सुधार)
Kya hota hai:
- अगर बाद में bugs आते हैं या users नए features माँगते हैं तो developers update करते हैं।
- इसमें:
- Bug fixing
- Performance improvement
- New feature add करना शामिल है।
Goal: Software को लंबे समय तक सही और updated बनाए रखना।
Waterfall Model कब Use करें (Best Case to Use):
- जब project छोटा हो और requirements बिल्कुल clear हों।
- जब कोई बदलाव की उम्मीद ना हो।
- जब technology पहले से जानी-पहचानी हो।
Examples:
- छोटे internal software tools
- College या academic projects
- Government या defense contracts — जहाँ हर चीज़ पहले से fix होती है
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?