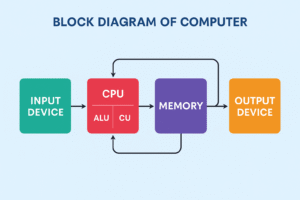
Block Diagram of a Computer – Explained in Simple Terms
The block diagram of a computer helps us understand the structure and working of a computer system. It shows the different parts (called components) of a computer and how they work together to process data.
In simple words, “A computer block diagram is a visual representation that shows how a computer works and what its main components are.”
With the help of this diagram, we can easily understand how computers perform tasks – from taking user input to giving output.
Let’s understand this with an example: Imagine a user gives some input to the computer and receives a result in return. The steps in between—how the input is processed and converted into output—can be clearly explained using the block diagram.
This diagram represents both the data entered by the user (input) and the data received as a result (output).
Main Components of a Computer
A computer has six main components:
- Input Device
- Output Device
- CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- CU (Control Unit)
- Memory
Let’s look at each of these in detail:
1. Input Devices
Input devices are the hardware tools we use to give commands or data to the computer. They allow users to interact with and control the computer.
The main job of input devices is to convert user input into binary language (0s and 1s), which the computer understands.
Functions of Input Devices:
- Accept input and commands from the user
- Convert the input into binary code
- Send the data to the computer for processing
Examples of Input Devices:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Microphone
- Scanner
- Trackball
- Joystick
- Webcam
2. Output Devices
Output devices display the results after the computer processes the input. In simple terms, they show us the final output.
They receive data from the computer and convert it into text, image, video, or sound format that users can understand.
Examples of Output Devices:
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speaker
- Projector
- Plotter
- Headphones
3. CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The CPU is often called the “brain” of the computer. It controls and manages all operations, processes data, and turns it into meaningful information.
It also handles all connected devices like the keyboard, mouse, and printer.
The CPU is the core component in the block diagram that receives input and produces output.
The CPU has two main parts:
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- CU (Control Unit)
4. ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
The ALU performs all mathematical and logical operations. It handles tasks like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as logic operations like AND, OR, and NOT.
5. CU (Control Unit)
The Control Unit manages and controls all parts of the computer system. It directs the flow of data between the memory, input/output devices, and the ALU.
It also ensures that instructions are followed in the correct order.
6. Memory
Memory is used to store data and instructions temporarily or permanently. It plays a major role in storing the data that the CPU needs to work with.
Types of Memory:
a) Primary Memory
Primary memory is directly accessed by the CPU. It is also known as main memory or internal memory.
Made of semiconductor materials, this memory is fast but volatile—meaning data is lost when power is off.
Primary Memory includes:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read-Only Memory)
b) Secondary Memory
Secondary memory stores large amounts of data permanently. Unlike primary memory, data in secondary storage is not lost when power is turned off.
The CPU cannot access it directly; the data must first be transferred to primary memory.
Examples of Secondary Memory:
- Hard drives
- SSDs
- USB drives
- CDs/DVDs
Block Diagram of Computer in Hindi – कंप्यूटर का ब्लॉक डायग्राम
कंप्यूटर का ब्लॉक डायग्राम कंप्यूटर के स्ट्रक्चर के बारें में बताता है। ब्लॉक डायग्राम हमें यह बताता है कि कंप्यूटर में कितने घटक (component) होते है और वे सभी एक दूसरे के साथ कार्य कैसे करते है।
दूसरे शब्दों में कहें तो, “कंप्यूटर का ब्लॉक डायग्राम एक स्ट्रक्चर होता है जो कंप्यूटर की कार्यविधि के बारें में जानकारी प्रदान करता है और यह भी बताता है कि इसमें कितने components होते हैं।”
कंप्यूटर ब्लॉक डायग्राम के द्वारा हम आसानी से समझ सकते हैं कि कंप्यूटर काम कैसे करता है और वह अपनी प्रक्रिया को कैसे execute करता है।
चलिए इसे उदहारण के माध्यम से समझते है:- मान लीजिये एक यूजर ने कंप्यूटर को कुछ इनपुट दिया और बदले में उसे कुछ आउटपुट प्राप्त हुआ, इस बीच में होने वाली प्रक्रियाओं को हम इस ब्लॉक डायग्राम के माध्यम से समझ सकते है।
यह डायग्राम यूजर के द्वारा दिए गए इनपुट डेटा और कंप्यूटर से प्राप्त किए गए आउटपुट डेटा को प्रस्तुत (represent) करता है।
कंप्यूटर के मुख्य रूप से 6 घटक (components) होते है: – CPU, इनपुट डिवाइस, आउटपुट डिवाइस, मैमोरी, ALU और CU.
नीचे आपको कंप्यूटर के ब्लॉक डायग्राम का चित्र दिया गया हैं –
Components of Computer in Hindi – कंप्यूटर के घटक
इसके 6 घटक होते हैं –
- Input Device (इनपुट डिवाइस)
- Output Device (आउटपुट डिवाइस)
- CPU (सीपीयू)
- ALU (ए.एल.यू)
- CU (सी.यू.)
- Memory (मैमोरी)
1- Input Device (इनपुट डिवाइस)
इनपुट डिवाइस ऐसे हार्डवेयर डिवाइस होते है जिनका इस्तेमाल यूजर के द्वारा कंप्यूटर को डेटा और निर्देश देने के लिए किया जाता है।
इनपुट डिवाइस के माध्यम से यूजर कंप्यूटर को कमांड या इनपुट देता है और बदले में आउटपुट प्राप्त करता है।
इनपुट डिवाइस की मदद से यूजर कंप्यूटर के साथ सीधे इंटरैक्ट करता है और कंप्यूटर को कण्ट्रोल करता है। इनपुट डिवाइस के कुछ लोकप्रिय उदहारण कीबोर्ड , माउस , स्कैनर आदि हैं।
कंप्यूटर केवल बाइनरी भाषा (0,1) को ही समझता है इसलिए इनपुट डिवाइस यूजर के द्वारा दिए गए डेटा और निर्देश को बाइनरी भाषा में बदलता है।
इनपुट डिवाइस के प्रमुख कार्य –
- यह यूजर से डेटा और निर्देश को लेता है।
- इसके बाद यह इस डेटा और निर्देश को बाइनरी भाषा में बदलता है।
- बाइनरी भाषा में बदले हुए डेटा और निर्देश को यह कंप्यूटर को भेज देता है।
Input device के उदाहरण –
- Keyboard (कीबोर्ड)
● Mouse (माउस)
● Microphone (माइक्रोफोन)
● Scanner (स्कैनर)
● Trackball (ट्रैकबॉल)
● Joystick (जॉयस्टिक)
● web cam (वेब केम)
2- Output Device (आउटपुट डिवाइस)
आउटपुट डिवाइस वे डिवाइस होते है जो यूजर के द्वारा दिए गए इनपुट को प्रदर्शित (display) करते है।
दुसरे शब्दो में कहे तो आउटपुट डिवाइस एक प्रकार का हार्डवेयर होता है जिसका इस्तेमाल आउटपुट डेटा को डिस्प्ले करने के लिए किया जाता है।
आउटपुट डिवाइस कंप्यूटर से डेटा को प्राप्त करते है और उस डेटा को टेक्स्ट, वीडियो और ऑडियो के फॉरमेट में बदल देते है।
Output device के उदाहरण –
- Monitor (मॉनिटर)
● Speaker (स्पीकर)
● Printer (प्रिंटर)
● Projector (प्रोजेक्टर)
● Plotter (प्लॉटर)
● Headphone (हेडफोन)
3- CPU (सीपीयू)
CPU का पूरा नाम Central Processing Unit (सेंट्रल प्रोसेस यूनिट) होता है। सीपीयू कंप्यूटर का दिमाग होता है। यह कंप्यूटर के सभी कामों को नियंत्रित करता है।
CPU को माइक्रोप्रोसेसर भी कहा जाता है, यह यूजर से प्राप्त डेटा को प्रोसेस करता है और इस डेटा को महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी में बदल देता है।
CPU कंप्यूटर से जुड़े सभी बाहरी डिवाइस (जैसे कि – कीबोर्ड, प्रिंटर या माउस) को कण्ट्रोल और मैनेज करता है ।
जिस प्रकार मनुष्य के पास दिमाग होता है बिना दिमाग के मनुष्य कुछ भी नही कर सकता, उसी प्रकार कंप्यूटर के पास CPU होता है। बिना CPU के कंप्यूटर कोई भी काम नही कर सकता।
ब्लॉक डायग्राम में, CPU को कण्ट्रोल यूनिट कहा जाता है। यह कंप्यूटर का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण घटक (component) है जो यूजर के द्वारा दिए गए इनपुट को प्राप्त करता है और उन्हें आउटपुट प्रदान करता है।
कंप्यूटर की सारी प्रक्रियाएं CPU में execute होती है। इसमें डेटा को प्राप्त करना, स्टोर करना और उसकी कैलकुलेशन करना जैसे कार्य शामिल है।
CPU की दो यूनिट होती है-
- ALU (ए.एल.यू)
- CU (सी.यू)
4- ALU (ए.एल.यू)
ALU का पूरा नाम आर्थमेटिक लॉजिक यूनिट (Arithmetic Logic Unit) होता है। यह सीपीयू का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा है इसका इस्तेमाल अंकगणितीय और तार्किक (logic) कार्यों को करने के लिए किया जाता है।
जोड़ना, घटाना, भाग करना, और गुणा करना आदि अंकगणित के कार्य होते हैं और AND, NOT, NOR आदि कार्य तार्किक होते हैं।
5- CU (सी.यू)
CU का पूरा नाम कंट्रोल यूनिट (control unit) है। कंट्रोल यूनिट कंप्यूटर से जुड़ी हुई सभी डिवाइसो और उनके कार्यों को नियंत्रित (control) करती है।
इसके साथ साथ कंट्रोल यूनिट Input Output कार्यो को भी नियंत्रित करती है। यह Memory और ALU के बीच हो रहे निर्देशो और डेटा के आदान प्रदान को control करने का कार्य भी करती है।
6- Memory (मैमोरी)
कंप्यूटर में डेटा और सूचना को स्टोर करने के लिए जिस डिवाइस का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है उसे मैमोरी कहते हैं।
मेमोरी कंप्यूटर का एक महत्वपूर्ण हिस्सा होता है जिसका काम डेटा और निर्देशों को कंप्यूटर में स्टोर करना होता है।
कंप्यूटर में memory दो प्रकार की होती हैं –
- Primary Memory (प्राइमरी मैमोरी)
- Secondary Memory (सेकेंडरी मैमोरी)
Primary Memory (प्राइमरी मैमोरी)
प्राइमरी मेमोरी एक प्रकार की कंप्यूटर मेमोरी है जिसे सीधे (direct) प्रोसेसर के द्वारा एक्सेस किया जाता है।
प्राइमरी मैमोरी कंप्यूटर की Main Memory होती है, जो CPU का एक हिस्सा होती है. CPU में लगे होने के कारण इस मैमोरी को आंतरिक मैमोरी भी कहा जाता है.
प्राइमरी मैमोरी को Semiconductor (अर्धचालक) पदार्थ से बनाया जाता है।
सरल शब्दो में कहे तो यह एक ऐसी मेमोरी है जिसका इस्तेमाल कंप्यूटर में मौजूद प्रोग्राम को स्टोर करने के लिए किया जाता है।
यह कंप्यूटर की मुख्य मेमोरी होती है जिसे प्राइमरी स्टोरेज के नाम से भी जाना जाता है। इसमें दो तरह की मेमोरी शामिल है RAM (रैंडम एक्सेस मेमोरी) और ROM (रीड ओनली मेमोरी) .
प्राइमरी मेमोरी कंप्यूटर के motherboard पर स्थित होती है और बिजली चले जाने पर इस मेमोरी में स्टोर डेटा खो जाता है।
यह मेमोरी महंगी होती है लेकिन सेकेंडरी मेमोरी की तुलना में डेटा को एक्सेस करने की गति (speed) तेज होती है।
Secondary Memory (सेकेंडरी मैमोरी)
यह भी एक प्रकार की कंप्यूटर मेमोरी है जिसे सीधे (direct) प्रोसेसर के द्वारा एक्सेस नहीं किया जा सकता।
सेकेंडरी मेमोरी एक ऐसी मेमोरी है जिसकी स्टोरेज छमता अधिक होती है और यह बड़ी मात्रा में डेटा को स्टोर कर सकती है।
इस मेमोरी का उपयोग बड़े आकार वाले डेटा जैसे (वीडियो, इमेज, ऑडियो, फाइल) को स्टोर करने के लिए किया जाता है।
इस मेमोरी में यूजर डेटा को आसानी से स्टोर कर सकता है और उस डेटा को पुनर्प्राप्त (restore) कर सकता है।
इस मेमोरी का उपयोग स्थाई (permanent) रूप से डेटा को स्टोर करने के लिए किया जाता है। permanent डेटा का अर्थ यह है की बिजली चली जाने के बाद भी डेटा बरकार रहे या डिलीट ना हो।
प्राइमरी मेमोरी में बिजली चली जाने पर डेटा खो जाता है परन्तु सेकेंडरी मेमोरी में ऐसा नहीं होता। CPU डायरेक्ट सेकेंडरी मेमोरी को एक्सेस कर सकता।
इसे ऐसा करने के लिए सेकेंडरी मेमोरी के डेटा को प्राइमरी मेमोरी में ट्रांसफर करना होगा इसके बाद CPU सेकडरी मेमोरी को एक्सेस कर पायेगा।
इसे सेकेंडरी स्टोरेज के नाम से भी जाना जाता है जो प्राइमरी मेमोरी की तुलना में सस्ती होती है।